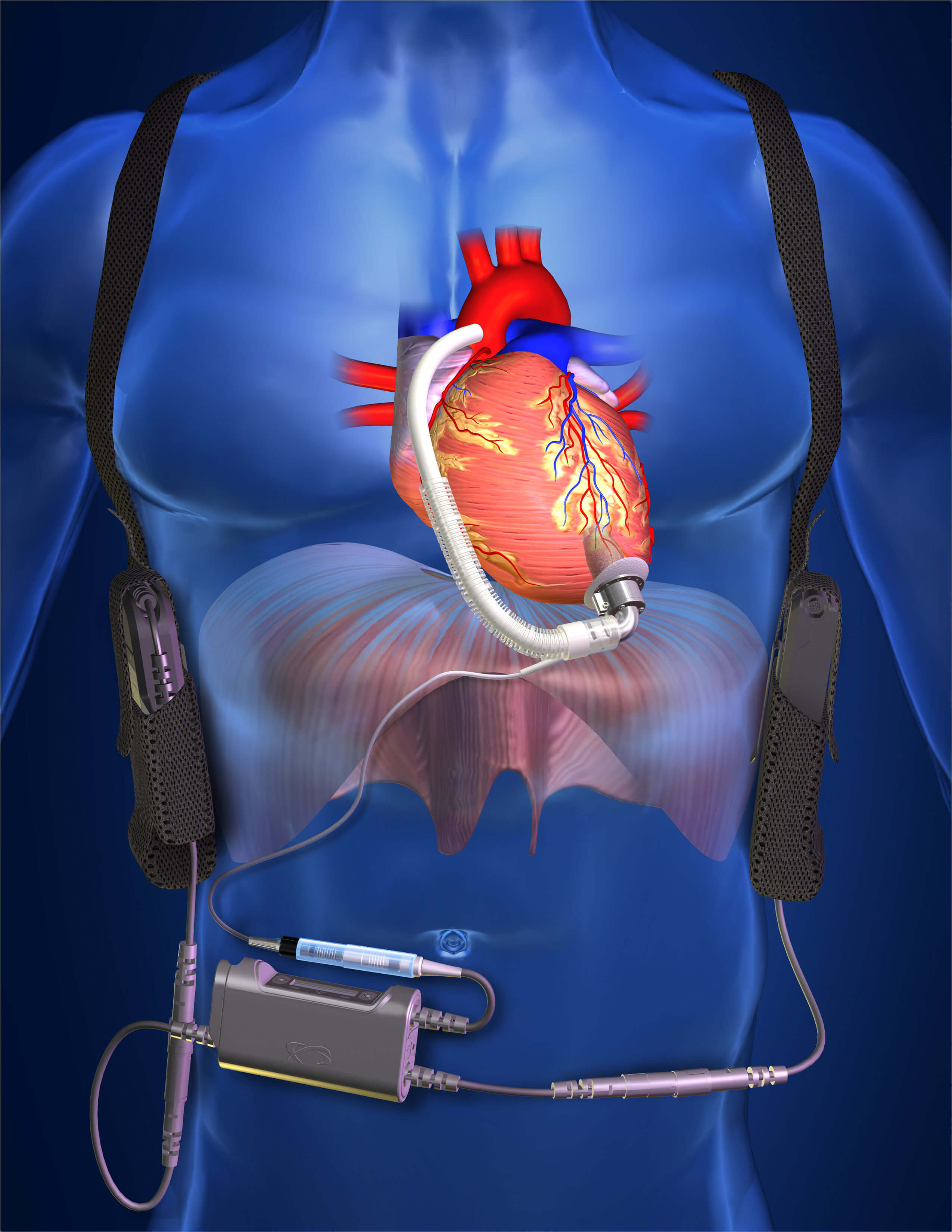

Collaboration between NASA and industry resulted in a lifesaving heart pump for patients awaiting heart transplants. The ventricular assist device functions as a "bridge to heart transplant" by pumping blood throughout the body. It has kept hundreds of critically ill patients alive until a donor heart became available. The device is small and can operate up to 8 hours on battery power, giving patients the mobility to do normal, everyday activities.
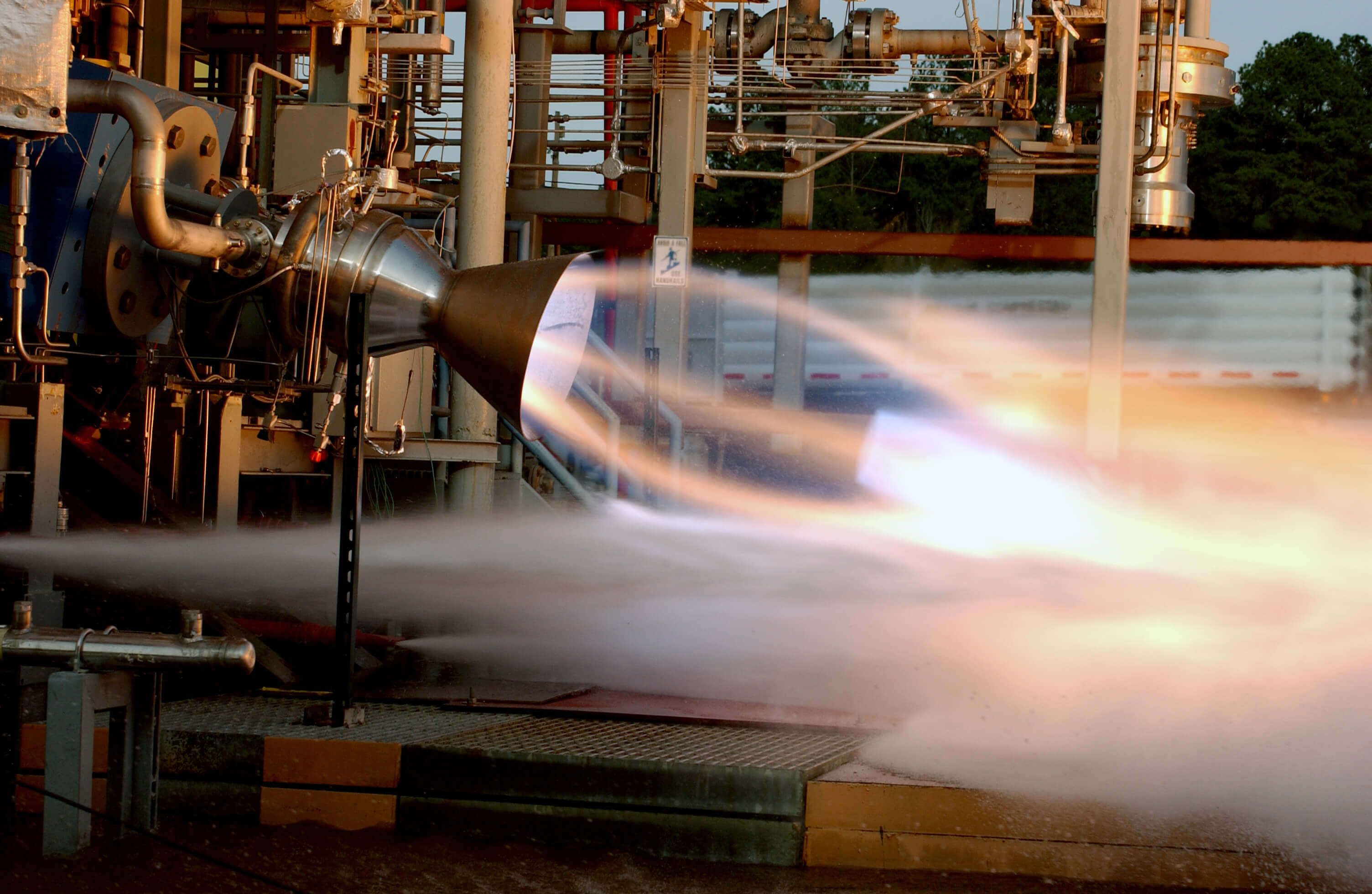
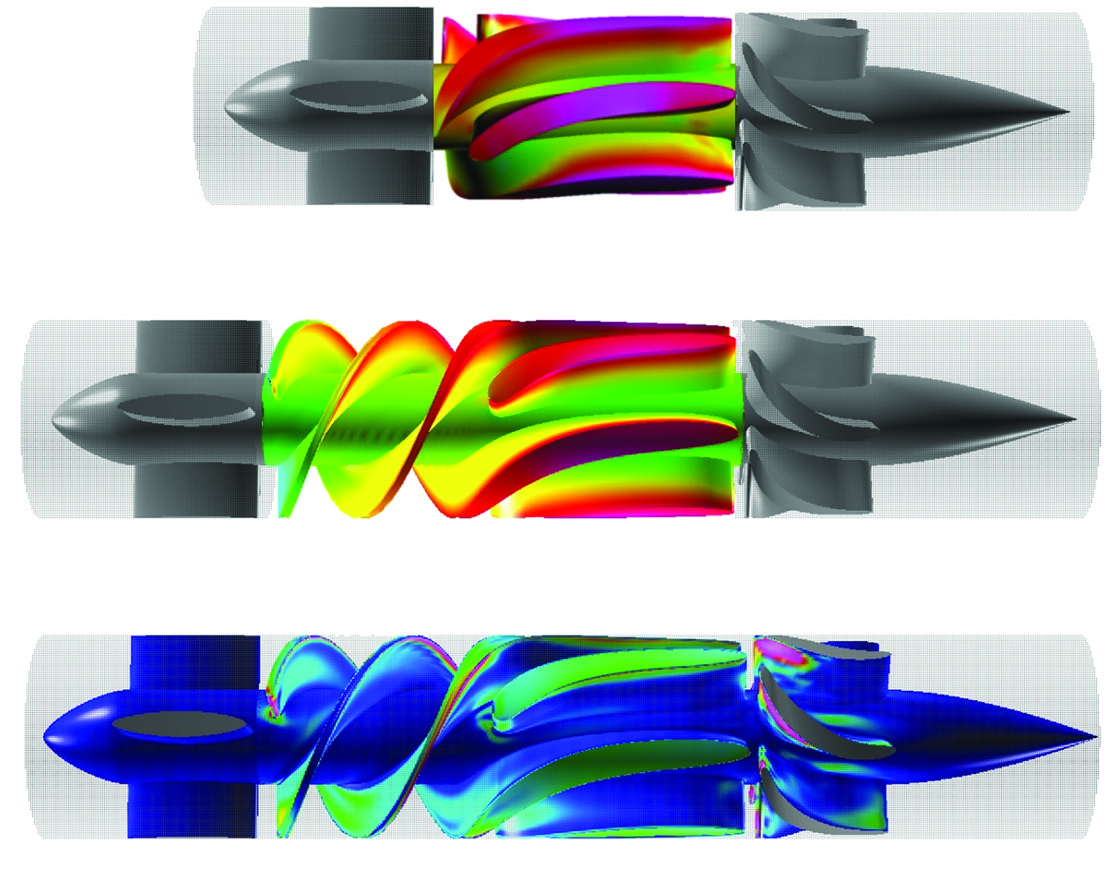
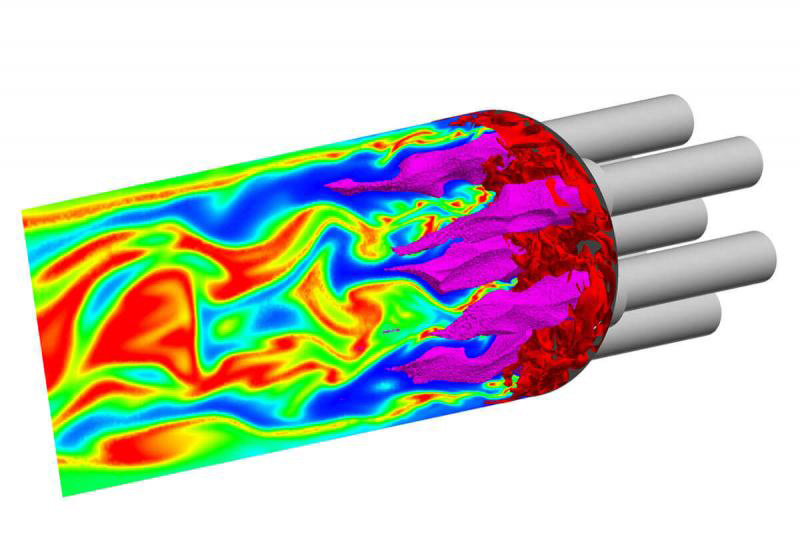
Medical experts from NASA partnered with industry to develop a ventricular assist device. The public-private team faced challenges with their initial design, and turned to an unusual source for help: another NASA team, this time a supercomputing division with expertise simulating rocket engines. It turns out that the flow of fluid through a rocket engine and the flow of blood through a heart share many similarities. The second NASA group was able to suggest multiple improvements to the prototype heart pump that helped make it safer and bring it to market.
Learn more about how NASA helped develop technology that impacts ventricular assist device within your city's medical environment!